When working with Angular’s new reactive features, particularly signals and effects, you might encounter issues when trying to update a signal outside the injection context. This article will guide you through resolving a common error you might face when using toSignal() in your Angular components, demonstrating how to refresh data effectively.
Problem Overview
You are trying to call a service method again to refresh data in your Angular component and convert the observable returned by the service into a signal using toSignal(). However, toSignal() has certain constraints—it can only be used within an injection context, such as:
- A constructor
- A field initializer
- A factory function
- A function used with
runInInjectionContext
Attempting to update a signal directly outside these contexts will result in an error like:
Error: toSignal() can only be used within an injection context such as a constructor, a factory function, a field initializer, or a function used with `runInInjectionContext`.
Solution
To resolve this, you can leverage Angular’s reactive programming features, such as using signals and effects, which provide a more structured and Angular-friendly way to handle such updates. Below is a practical solution to handle this scenario effectively.
Implementation Guide
Here is a solution implemented using BehaviorSubject to manage refresh triggers and toSignal() within the constructor’s injection context:
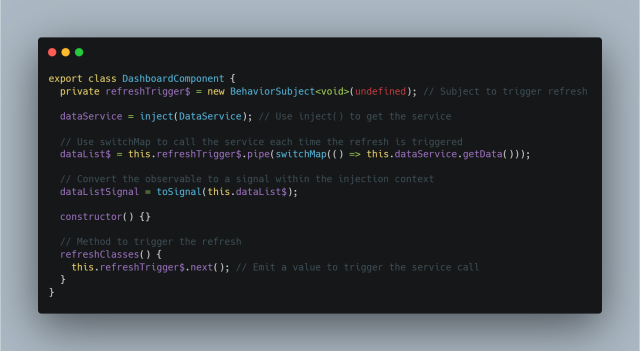
Step-by-Step Explanation
BehaviorSubjectfor Refresh Trigger:- A
BehaviorSubjectis used to create a trigger that manages when the service method should be called again. This approach allows you to easily manage and re-emit values to refresh data.
- A
- Service Injection:
- The
DataServiceis injected using Angular’sinject()function to provide the service dependency.
- The
- Handling Data Fetch with
switchMap:- The observable
dataList$is defined usingswitchMap. Each time the refresh trigger emits, the service methodgetData()is called, ensuring the latest data is always fetched.
- The observable
- Using
toSignal()in the Injection Context:toSignal()converts thedataList$observable into a signal, and this conversion is performed within the constructor or a field initializer, ensuring that it stays within the proper injection context.
- Refreshing the Data:
- The
refreshClasses()method calls.next()on theBehaviorSubject, effectively triggering theswitchMapto fetch new data and update the signal.
- The
Why This Solution Works
By using the BehaviorSubject and managing the data fetching logic with switchMap, this approach adheres to Angular’s reactive principles. toSignal() is utilized correctly within the injection context, which avoids the context-related errors and maintains a clean, reactive workflow in your component.
Key Takeaways
- Reactive Approach: This approach keeps your component reactive, maintaining clean separation between data-fetching triggers and the actual data-handling logic.
- Proper Usage of
toSignal(): EnsuretoSignal()is used within the correct context to avoid injection errors. - Simplicity and Control: This method provides a straightforward way to control when your data is refreshed without overly complex state management.
Implementing this pattern helps you effectively manage data updates in Angular while avoiding common pitfalls with reactive programming in Angular’s new signal-based paradigm.
